PlotterController
Program for controlling XY41xx plotters.
1 Table of contents
2 Introduction
The aim of PlotterController project is to develop portable controlling program for XY41xx plotters and other small plotters. Project is written in C programming language with focus on portability and extensibility.
3 Hardware supported
3.1 Currently supported hardware
3.1.1 Raspberry PI -> GPIO -> XY41xx
Raspberry PI works with 3.3V whereas XY41xx works with 5V. For this reason you cannot conect Raspberry directly to XY41xx - this would damage your Raspberry. See below how to connect it.
3.1.2 Linux PC -> /dev/parportx -> XY41xx
You only need to make sure you have permission for reading from and writing to /dev/parportx device. If you cannot see /dev/parport0 you can try run:
$ sudo modprobe ppdev
3.1.3 FreeBSD PC -> /dev/ppix -> XY41xx
Again you only need to make sure you have permission for reading from and writing to /dev/ppix device.
3.1.4 DOS -> LPTx -> XY41xx
This port is tested well with Borland Turbo C 2.01 which is available for free:
http://edn.embarcadero.com/article/20841
- use turbo c and file PLOTTER.PRJ which is located in src directory
- make sure font1.fnt is present in the same direcroty as PLOTTER.EXE
- this should be working with any kind of DOS OS
3.1.5 MS Windows -> LPTx -> XY41xx
This port is not supported yet. In some versions of Winows OS you need additional software (such as userport or porttalk22) for enabling direct access to LPTx ports. See following links:
http://hw-server.com/parallel-port-lpt-ieee-1284#xp
http://www.drdobbs.com/184409876
3.2 Interfaces
3.2.1 Raspberry PI GPIO
Raspberry PI works with 3.3V whereas XY41xx works with 5V. For this reason you cannot conect Raspberry to XY41xx directly - this would destroy your Raspberry. You will need following transistor interface:
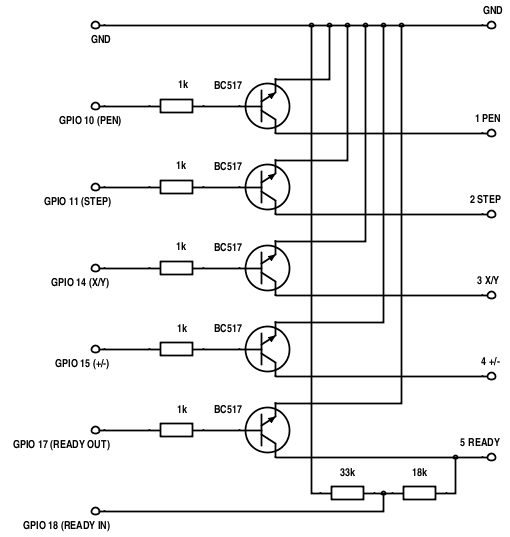
If you have Raspberry Pi, Pi Zero, Pi Zero W or Compute Module use following printer creation:
PRINTER *prn = pr_create_printer(GPIO, "1");
In case of Raspberry Pi 2, Pi 3 and Compute Module 3 use:
PRINTER *prn = pr_create_printer(GPIO, "2");
3.2.2 PC Parallel port
There is also available connection through parallel port with following configuration:
PLOTTER
PC-printer port XY4131 XY4140 XY4150
bit 2 4 ------------------ 1 ----------- 1 ----------- 1 PEN
bit 3 5 ------------------ 2 ----------- 2 ----------- 2 STEP
bit 1 3 ------------------ 3 ----------- 3 ----------- 3 X/Y
bit 0 2 ------------------ 4 ----------- 4 ----------- 4 +/-
bit 4 6 ------------------ 5 ----------- 5 ----------- 5 READY
GND 18 ------------------ 6 ----------- 6 ----------- 6 GND
For Linux PC use:
PRINTER *prn = pr_create_printer(PARPORT, "/dev/parport0");
FreeBSD PC use:
PRINTER *prn = pr_create_printer(PARPORT, "/dev/ppi0");
DOS PC use:
PRINTER *prn = pr_create_printer(PARPORT, "0x378");
4 Usage
4.1 Building of project
For building of project follow these steps:
- Download project
git clone https://github.com/berk76/plottercontroller PlotterController - Go into project directory
cd PlotterController - Run
make - Find following binaries:
plotter_controller,prn_hpgl - You can run
plotter_controllerand try demos or you can draw hpgl files usingprn_hpgl
4.2 Drawing HPGL files
Now you can draw any HPGL file using prn_hpgl command.
Usage:
prn_hpgl [-s <scale factor>] -i <interface number> -f <file.hpgl>
Interface numbers available:
(1) Linux PC (/dev/parport0)
(2) FreeBSD PC (/dev/ppi0)
(3) DOS PC (0x378)
(4) Raspberry Pi, Pi Zero, Pi Zero W and Compute Module
(5) Raspberry Pi 2, Pi 3 and Compute Module 3
For example if you have plotter connected through parallel port to Linux you can run:
$ ./prn_hpgl -i 1 -f hpgl_examples/kuzeloid.hpgl
If you have HPGL file which doesn’t match drawing size of your plotter you can use fit_hpgl command to resize it:
Usage:
fit_hpgl [-i] -x <new x size> -y <new y size> -f <file.hpgl>
-i print info only
-f input file
-x new x size
-y new y size
Using this utility you can convert HPGL file and resize it to match provided size and save it to file:
$ ./fit_hpgl -x 2500 -y 1750 -f hpgl_examples/kuzeloid.hpgl > saved.hpgl
or you can pipeline output directly to prn_hpgl:
$ ./fit_hpgl -x 2500 -y 1750 -f hpgl_examples/kuzeloid.hpgl | ./prn_hpgl -i 1
You can find more HPGL pictures and examples at cygnus.speccy.cz …
4.3 Programming
Plotter controller is implemented as C library supporting drawing functions.
Example of usage:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "printer.h"
#include "graph.h"
#include "text.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
PRINTER *prn;
if ((prn = pr_create_printer(GPIO, "2")) == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Cannot access port\n");
return -1;
}
pr_init(prn); /* Initialization */
POSITION paper = pr_get_max_position(prn);
xy_vr(prn, paper.x, 0); /* Vector Relative */
xy_vr(prn, 0,paper.y);
xy_vr(prn, -paper.x,0);
xy_vr(prn, 0,-paper.y);
xy_vr(prn, paper.x,paper.y);
xy_mr(prn, 0,-paper.y); /* Move Relative */
xy_vr(prn, -paper.x,paper.y);
xy_set_font_size(8); /* Set Font Size */
xy_set_text_angle(M_PI_2); /* Set Text Orientation */
xy_ma(prn, paper.x - 100, 100); /* Move Absolute */
xy_vs(prn, 7); /* Velocity Set */
xy_write(prn, "Hello World!"); /* Draw text */
xy_hm(prn); /* Takes pen home */
pr_close_printer(prn);
return 0;
}
See main.c file for more examples.
See API documentation for complete set of functions available.
5 Architecture
In order to be PlotterController well extensible it is layered into following logical parts:
+---+--------------------+
| 5 | Client program |
+---+------+------+------+
| 4 | Text | HPGL | |
+---+------+------+ |
| 3 | Graph |
+---+--------------------+
| 2 | Printer |
+---+---------+------+---+
| 1 | Parport | GPIO |...|
+---+---------+------+---+
5.1 Interface Layer
Interface layer currently implements parallel port and GPIO I/O. It depends on Operating System and computer platform used. If you want to add support for new interface this layer is right place for it.
5.2 Printer Layer
Printer layer implements particular plotter. If you want to add support for another device you should do it at this layer.
See API for more info…
5.3 Graph Layer
Graph layer implements basic support for graphics drawing. You can implement new basic drawing features such as new graphical primitives, line types and so on here.
See API for more info…
5.4 Special Graph Layer
This layer implements special graphics modules like support for text drawing, support for HPGL and so on.
See API for more info…
5.5 Client program
Client program (or application) works directly with basic graphics library and with special graphics modules (text, HPGL).
6 Support
Do you have question or idea? Visit discussion.

